Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disorder
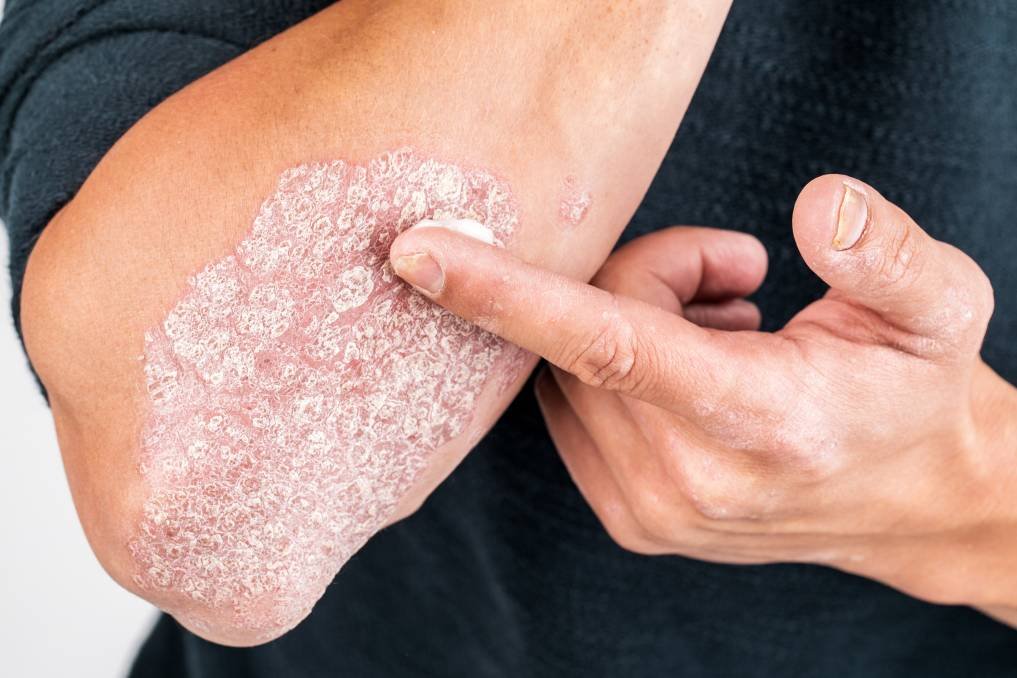
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disorder that causes the skin cells to rapidly build up on each other leading to the formation of itchy scaly plaques on the skin. They commonly occur on the elbows, knees, hands, feet, lower back, belly button, scalp, and ears. Psoriatic scales are typically whitish silver developing in thick red plaques. However, they can appear more purplish or dark brown with grayish scales on darker skin tones. Psoriasis can also affect the nails and joints, leading to psoriatic arthritis.
A chronic disease without cure, psoriasis can be quite painful and make life difficult. It is characterized by periods of flare-ups and periods of remission.
About 3% of the American population suffers from psoriasis.
Causes of Psoriasis
Despite the lack of a specific cause, there are two key factors that play an important role in psoriasis.
· Genetics: There is an increased risk of having psoriasis if you have an immediate family member with it.
· Immune system: Autoimmune conditions arise from the body attacking itself. Being an autoimmune condition, psoriasis is characterized by white blood cells known as T cells erroneously attacking your skin cells and, in some cases, the joints.
Types of Psoriasis
·Plaque psoriasis: This is the most common type, affecting about 80-90 percent of people living with psoriasis. It is characterized by inflamed, itchy, scaly plaques on the skin.
·Pustular psoriasis: Pustular psoriasis causes tiny white, pus-filled blisters overlying broad areas of inflamed, red skin.
·Guttate psoriasis: This type is more common during childhood and presents with smaller, thinner, pink, round, scaly patches. It can be triggered by infections, streptococcus infections being a well-known cause.
·Inverse psoriasis: Inverse psoriasis causes prominent areas of shiny and inflamed skin in skin folds such as the armpits, breasts, and groin.
·Erythrodermic psoriasis: This is a severe and rare type that covers the entire body at once and presents with total body redness and scaling. Fever is a common feature of this type, and it can be life-threatening.
Common Symptoms of Psoriasis
There are different types of psoriasis, however, some common symptoms include
Inflamed scaly patches of skin
Cracked dry skin with a tendency to bleed
Itchy skin
Stiff and swollen joints
Psoriasis Triggers
Knowledge of the triggers of psoriasis will help you avoid them if you are predisposed to having psoriasis. These triggers are as follows:
Stress
Alcohol
Injury
Certain medications e.g., Lithium, certain antimalarials
Infections, commonly streptococcal infections
Smoking
Treatment of Psoriasis
Psoriasis can often be diagnosed by clinical examination alone, or if needed, via a skin biopsy. Treatment of psoriasis is usually varied, depending on the type and severity. The more parts of the body affected, the more involved the treatment is. The good news is there are now numerous treatment options available.
Treatment is aimed at decreasing inflammation. Typical first-line treatments for psoriasis with limited involvement of the skin only include potent topical steroids, topical vitamin D creams, topical calcineurin inhibitors, or topical retinoids. For more widespread disease, ultraviolet light therapy is often used.
In moderate to severe psoriasis affecting more than 10% of body surface area, or in psoriatic arthritis, systemic oral medications can be used, which include systemic retinoids or disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, mycophenolate mofetil, and azathioprine.
More recently, however, newer injected immune-modulating drugs have become available. These drugs have been life-altering for patients suffering from psoriasis because they target specific pathways of inflammation in psoriasis and thus have fewer side effects and are more efficacious than some of the older oral medications. These drugs include tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha inhibitors such as adalimumab (Humira), IL-17 inhibitors like ixekizumab (Taltz), and IL-23 inhibitors such as risankizumab (Skyrizi).
Psoriasis Treatment in Sugar land, Texas
Determining the right treatment for your psoriasis requires a board-certified dermatologist who can assess the type and severity of psoriasis. The dermatologist will also need to understand the patient's coexisting conditions and have a strong grasp on the use and side effects of the many medication options.
At Sweetwater Dermatology in Sugar Land, Texas, our dermatologist, Dr. Likhari, has the experience and expertise to accurately assess the type and severity of your psoriasis and guide you through the options to select the best for you.
Call 832-615-3201 to schedule an appointment to discuss your psoriasis with Dr. Likhari or request an appointment online.